#Industry News
WHAT A CODE RED MEANS TO HOSPITAL SAFETY AND PATIENT LIVES
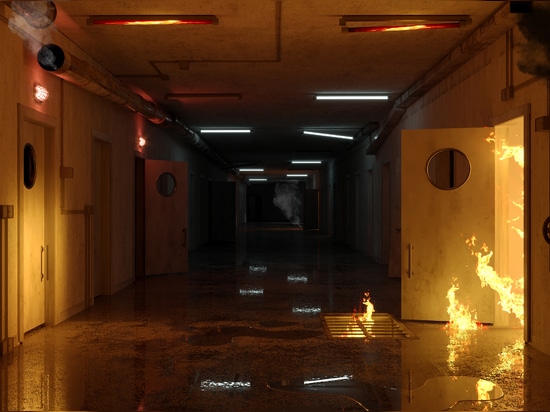
Dealing with on-site fires and similar emergencies
A hospital emergency code is a special alert used by hospital staff. It is triggered primarily to indicate an urgent matter or some emergency matter.
The codes are not blatantly announced (example: “heart attack”, “bomb threat”, “missing baby”, etc.) This is to prevent panic or distress among patients and visitors. Instead they’re given a color or some other unassuming signal. The most well-known hospital code is Code Blue.
What is a Code Red in a Hospital?
A Code Red is another hospital emergency code. It means a hospital has reason to believe there is a fire on the premises. Staff may activate it due to:
Actually seeing the fire or smoke.
Smelling the fire or smoke.
Doors or walls feel hot to the touch.
What Happens During a Code Red in a Hospital?
Medical staff handle a Code Red. First one activates one of the fire alarms located throughout the hospital. A staff member at the nursing station or similar location then calls out the code through the intercom system. This includes the fire’s location (“Code Red NICU”.) This is repeated usually three times depending on the hospital’s procedures.
Some healthcare facilities use a different tactic. Instead of activating a fire alarm, they may quietly alert staff first via their mobile devices like pagers, smartphones, or medical tablets. This allows the hospital to start the R.A.C.E. system (see below) before the alarm goes off and the announcement is made overhead. This two-step process heads off any panic and confusion from patients and visitors.
The R.A.C.E. system is used during Code Red. It prioritizes what hospital staff are to do during the emergency.
“R” stands for Rescue. Steps involved in this part include:
Help people in immediate danger.
Move anyone who has been injured by the fire when it’s safe to do so.
Move critical patients with their life-sustaining IVs or other forms of medical equipment.
Open / close doors as per procedure.
Perform a headcount / roll call to make sure all patients and personnel are accounted for.
Evacuation methods to move non-mobile patients include:
Bed transfer (i.e., rolling them out in their hospital bed)
Cradle drop (wrapped into a blanket which is then dragged out by staff)
Use of a medical sled called a paraslyde
Via a stair chair
Non-life-sustaining items like personal belongings are left behind.
“A” stands for Alarm and is the step when the fire alarm is activated. The Code Red announcement, from who’s authorized to make it and how many times, is found under this procedure. Same with any special phone numbers to first responders to contact (example: fire department).
“C” stands for Confine. At this point:
Hallways are cleared of staff and visitors.
Doors within easy reach are closed. This helps confine the fire from growing into other parts of the hospital.
Medical staff and patients are to stay between fire-barrier doors and areas. And if anyone goes to a new area, they are to first touch any new door for heat.
HVAC systems are turned off.
“E” stands for Extinguish. Medical personnel at this part of the procedure aim to try to stop the fire while waiting for firefighters to arrive.
Usually one staff member per floor in the healthcare facility may be assigned to fight the fire.
They are to use the nearest fire extinguisher they have access to before heading to the site.
At the site of the fire, use the P.A.S.S. procedure as per the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. The following are performed at this stage:
P Pull the pin
A Aim for the base of the fire
S Squeeze the handle of the fire extinguisher
S Sweep from right to left and vice versa across the base of the flames
The entire process is repeated if the fire reignites.
In the US, staff in hospital departments outside of the fire area do not immediately start to evacuate. Instead they remain in their departments. They stay close to their patients and wait for a Code Green. This code indicates it’s time to evacuate as per the above R.A.C.E. procedures.
In medical clinics, the process is slightly different. Many times there is no declaration of a Code Red. Instead, once the fire alarm goes off, the visitors are escorted to fire exits.
A Code Red ends when authorized medical personnel announce an all clear signal.
Medical Computers During a Code Red
Medical computers can be quite useful when dealing with a Code Red. Healthcare IT should consider the following features:
Medical grade - Medical grade PCs which have been tested and certified to be safe for near-patient use. This includes being tested for hazards like causing fire and igniting from flammable anesthetics.
Fanless design - Many medical computers stay cool using a fanless design. That means no smoke could be drawn in and damage the delicate interior.
IP65 rated - The front bezel of the medical computer is sealed against liquids. This makes it easy for hospital staff to later clean any undamaged computers with harsh liquid cleaning chemicals and detergents.
Closing Thoughts
Emergency medical codes are used in healthcare to notify staff of urgent matters without triggering a panic among patients and visitors. Hospitals use Code Red if they suspect a fire is somewhere onsite.
A Code Red is sent out if medical staff suspect the presence of smoke or fire somewhere on the premises. Once the alert is announced, sent out, or both, Medical personnel use various procedures like R.A.C.E. to deal with such a danger.
Contact an expert at Cybernet if your medical practice wants to learn how medical computers can be used in dealing with Code Red alerts and R.A.C.E. processes.