#Industry News
Better and Faster Results: The Power of Edge Computing in Healthcare
Edge computing promises to help deliver faster and more effective healthcare for those that need it.
With over 10 billion Internet of Things (IoT) medical devices in use today, managing and using the data they generate has never been more important.
However, how and where this data is collected and processed is a significant point of contention. Most healthcare organizations rely on cloud-based computing solutions, where data is transmitted to a centralized server for use.
Edge computing has risen as an attractive alternative to cloud computing. Properly implemented, edge computing can deliver faster, more accurate results, leading to better patient outcomes.
Cloud Computing vs. Edge Computing: What’s the Difference?
Cloud computing: In cloud computing, data is collected and transmitted to a centralized server for processing and analysis. This data is pulled from clinics, EMS units, wearable sensors, and in-home devices.
Doing this does have several disadvantages, however. First, transmitting this data requires sending it through a central firewall, which inspects and verifies it before it can reach the cloud for processing. However, passing through this firewall takes time, time that may be critical in a healthcare environment.
The second major downside is that malicious actors can intercept or spy on the data while it is transmitted. This forces healthcare groups to use some form of encryption to protect their data and ensure HIPAA compliance. Encrypting and decrypting data is also costly in terms of time.
Edge computing: In an edge computing environment, data collection and processing occur on the same local area network (LAN). This could be two devices physically connected, such as a pacemaker directly plugged into a medical-grade computer or processors built directly into the medical device itself.
The Advantages of Edge Computing in Healthcare
By being placed closer to the source of the data itself, edge computing enjoys several advantages over conventional computing or cloud-based solutions.
Improved Patient Care
Because health data can be analyzed faster, healthcare providers and patients can react to potential issues before they become major problems. This speed also helps ensure diagnoses are more accurate to patients’ needs.
Security and Privacy Compliance
Processing data at its collection site removes the need for transmission to a cloud service. This means there’s less need to encrypt it, making it easier to meet data privacy regulations like HIPAA.
Lower Costs
Healthcare groups can save money by not having to license expensive cloud services. Additionally, edge computing's accuracy helps prevent mistakes and lowers the cost per patient.
Use Cases for Edge Computing
Edge computing is best used in places that require quick diagnosing or reaction to changes in a patient’s condition, such as:
Ambulances
In most current emergency service systems, paramedics can only brief doctors and get patients the treatment they need once they reach the hospital. This means critical minutes where a patient needs treatment but cannot receive it go to waste. With edge-computing devices, first responders can analyze a patient’s vital signs for real-time diagnosis and treatment.
In-Hospital Patient Monitoring
Patient monitoring devices such as glucose and heart rate monitors are either unconnected or have to be linked to a third-party cloud service. Unfortunately, using these cloud services presents the aforementioned speed and security concerns. On-site edge computing can process data locally, answering both of these problems.
Remote Patient Monitoring and Care
Telehealth’s remote patient monitoring (RPM) is an attractive proposition for healthcare groups, as it allows them to send patients home earlier, lowering costs and freeing up beds. It’s also extremely useful for serving remote or rural areas where accessing medical resources is difficult.
By using edge computing medical devices in their remote patient monitoring, healthcare groups can provide patients with real-time information on their condition. Implementing edge computing here also reduces the need to transmit data across long distances, which can be incredibly demanding on rural networks (especially if video is being sent).
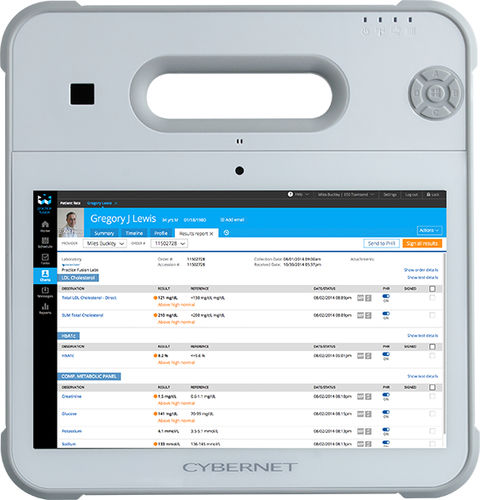
Edge Computing With Cybernet Medical Computers
While taking advantage of edge computing can require powerful equipment, it also comes with numerous advantages that make it a natural fit for the healthcare world. If you're looking for medical-grade computers and tablets that are certified for healthcare environments and boast powerful Intel processors and up to 64 GB of RAM. This allows them to take on even the most challenging edge computing applications.
If you’d like to learn more about the benefits of edge computing and how Cybernet’s devices can help you achieve it, feel free to contact our team. We’d be happy to discuss how our devices can support your organization’s efforts to modernize its healthcare operations.