#Product Trends
Operating Room Equipments: Brief Description
Keywords: "operating room equipments"; "surgical table"; "operating room light"
I. Introduction
Operating room equipment is essential for successful surgical procedures. Two of the most important components of the operating room are the surgical table and operating room light. The surgical table is where the patient lies during surgery and must be comfortable, adjustable, and sturdy enough to hold the patient's weight. The operating room light is used to illuminate the surgical site and must provide bright, clear light without casting shadows or causing eye strain.
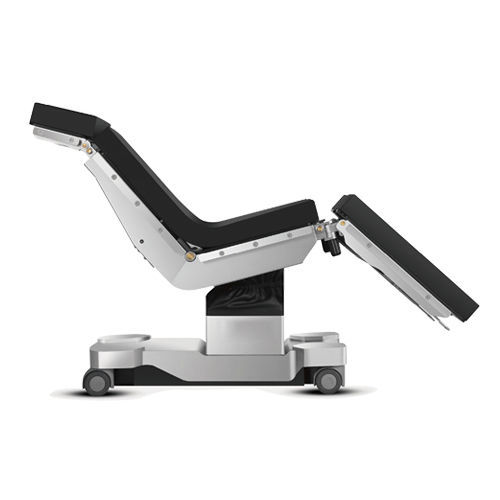
The surgical table is available in different types and models, each designed for specific purposes. There are general surgical tables, orthopedic tables, radiolucent tables, and others. General surgical tables are versatile and can be used for various types of surgeries. Orthopedic tables, on the other hand, have additional features such as leg and hip supports for specific surgical procedures. Radiolucent tables allow for X-rays to be taken without moving the patient, reducing the risk of surgical complications.
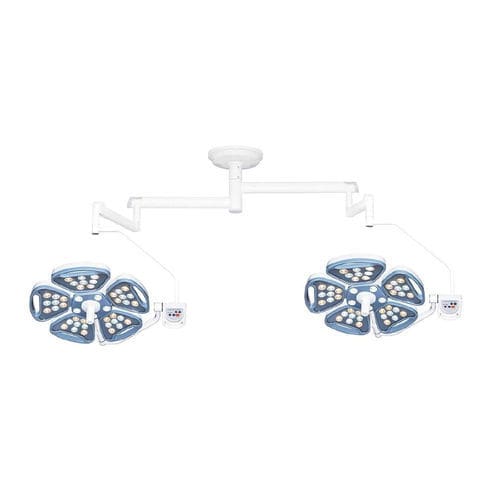
The operating room light is also available in different types and models, each with specific features and benefits. LED lights are becoming increasingly popular as they provide bright, clear light without generating excessive heat or requiring frequent bulb replacements. Other features to consider when choosing an operating room light include color temperature, intensity, and focus.
Ⅱ. Key Components of the Operating Room
Surgical Table: Types, Features, and Benefits
The surgical table is an essential component of the operating room and is designed to provide support and positioning for the patient during surgery. There are various types of surgical tables available, each with unique features and benefits.
General surgical tables are the most common type of surgical table and are designed for use in a wide range of surgical procedures. They have adjustable height, tilt, and positioning options to accommodate various surgical positions, and are typically made from durable materials that can withstand heavy loads.
Orthopedic tables are designed for use in orthopedic surgeries, such as joint replacement procedures. They have additional features such as traction devices, leg and hip supports, and are designed to support the weight of larger patients.
Radiolucent tables are designed for use in procedures that require imaging, such as X-rays or CT scans. They allow for easy imaging without the need to move the patient, reducing the risk of complications.
Operating Room Light: Types, Features, and Benefits
The operating room light is another critical component of the operating room and is used to illuminate the surgical site. There are various types of operating room lights available, each with unique features and benefits.
LED lights are becoming increasingly popular as they provide bright, clear light without generating excessive heat or requiring frequent bulb replacements. Other types of lights include halogen lights and xenon lights, which provide bright, white light with excellent color rendering.
When choosing an operating room light, features such as color temperature, intensity, and focus should be considered. The light should also provide an adequate light field without causing shadows or eye strain.
Anesthesia Machines and Ventilators: Functions and Benefits
Anesthesia machines and ventilators are used to deliver anesthesia and oxygen to patients during surgery. Anesthesia machines are designed to provide a precise and consistent flow of anesthesia gases to the patient, while ventilators are used to support the patient's breathing during surgery.
Anesthesia machines typically include a ventilator, vaporizer, and breathing circuit. They may also include monitoring devices such as a pulse oximeter, capnograph, or blood pressure monitor.
Ventilators are available in various types, including invasive and non-invasive ventilation. Invasive ventilation involves placing a breathing tube down the patient's throat, while non-invasive ventilation involves the use of a mask or nasal prongs.
Medical Imaging Devices: Types and Benefits
Radiotherapy EquipmentMedical imaging devices are used to generate images of the patient's internal structures, such as bones, organs, and tissues. They are commonly used in diagnostic and interventional procedures.
Some of the most common types of medical imaging devices include X-ray machines, CT scanners, MRI machines, and ultrasound machines. Each type of device has unique benefits and limitations.
X-ray machines are commonly used to image bones and are widely available. CT scanners provide detailed images of internal organs and tissues, while MRI machines use magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images. Ultrasound machines use sound waves to create images and are commonly used in obstetrics and gynecology.
In addition to their unique capabilities, medical imaging devices offer a range of benefits to patients and healthcare providers. For example:
Early detection of diseases: Medical imaging devices can detect diseases in their early stages, which can lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes.
Non-invasive procedures: Many medical imaging devices are non-invasive, meaning they do not require surgery or other invasive procedures. This can reduce the risk of complications and lead to faster recovery times.
Improved accuracy: Medical imaging devices can provide highly accurate images, allowing healthcare providers to make more informed diagnoses and treatment plans.
Reduced need for exploratory surgery: With the use of medical imaging devices, healthcare providers can often avoid exploratory surgery, which can be time-consuming, expensive, and risky.
Customized treatment plans: Medical imaging devices can provide detailed images of a patient's anatomy, allowing healthcare providers to customize treatment plans to each patient's unique needs.
Reduced radiation exposure: Some medical imaging devices, such as MRI machines, do not use ionizing radiation, which can be harmful in high doses. This can reduce the risk of radiation exposure for both patients and healthcare providers.
III. Common Challenges and Limitations
Despite the advancements in technology and the availability of state-of-the-art equipment, there are still common challenges and limitations that the operating room faces. Some of these include:
hospital doctorSpace constraints: Operating rooms are often limited in space, which can make it difficult to accommodate all the necessary equipment and personnel. This can lead to a cramped environment, which can increase the risk of accidents and errors.
Infection control: Infections are a major concern in the operating room, and it is essential to maintain a sterile environment to prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses. However, it can be challenging to keep the operating room completely sterile, particularly during long and complex procedures.
Equipment failure: Like any equipment, operating room equipment can fail, which can lead to delays, cancellations, and even patient harm. It is important to have regular maintenance and checks to ensure that all equipment is functioning properly.
Cost: Operating room equipment can be expensive, and many hospitals and clinics may struggle to afford the latest and most advanced equipment. This can limit the options available and may affect the quality of care that patients receive.
Training and education: The use of advanced operating room equipment requires specialized training and education. It is important to ensure that all personnel are adequately trained to use the equipment properly, and ongoing education and training are necessary to keep up with new developments and technologies.
Patient safety: Ultimately, patient safety is the most critical concern in the operating room. Despite the best efforts of healthcare professionals, there is always a risk of complications, errors, and adverse events. It is important to continually monitor and evaluate procedures and equipment to minimize these risks and ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
IV. Future of the Operating Room
As the healthcare industry continues to advance, the future of the operating room looks bright with the introduction of emerging technologies that are set to revolutionize how surgeries are conducted. These technologies promise to enhance the capabilities of existing operating room products, improve surgical precision, and reduce the risk of human error.
One of the most significant areas of innovation is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics into the operating room. AI can be utilized in various ways, such as to analyze patient data, predict potential complications, and assist with decision-making during the surgery. With machine learning algorithms, AI can analyze vast amounts of patient data to make predictions about the likelihood of complications, and even provide guidance during surgery, reducing the chances of human error.
Robotics is also an area of great potential in the operating room. Robotic-assisted surgery is becoming increasingly common, with robots assisting with procedures such as prostatectomies, hysterectomies, and joint replacements. Robotic surgery offers several benefits, including greater precision, smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times.
In addition to AI and robotics, other emerging technologies are also set to impact the future of the operating room. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies have already begun to be utilized in surgical training, allowing surgeons to practice procedures in a realistic simulated environment. 3D printing technology is also being explored as a means of creating patient-specific implants and prosthetics.
Overall, the future of the operating room is bright, with emerging technologies set to transform the capabilities of operating room products and improve patient outcomes. The integration of AI, robotics, AR, VR, and 3D printing technologies will undoubtedly lead to safer, more efficient, and more effective surgical procedures.