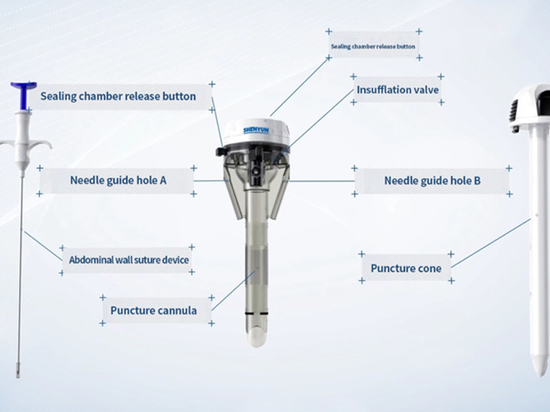
#Industry News
Gastric bypass vs gastric sleeve, which one is better? Meta-analysis of 20 high-evidence RCTs with a total of 1270 patients|Obesity Surgery
shenyun medical
In the battle against obesity, researchers are constantly searching for the most effective and safest solutions. A comparison between two surgical methods, laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG). The researchers selected clinical comparative RCTs of LRYGB and LSG for analysis. The results Published in Obesity Surgery, the official journal of the International Federation for Obesity and Metabolic Surgery (IFSO).
Key Takeaways:
1. LRYGB is superior to LSG in terms of short-term and mid-term weight loss effects, short-term type 2 diabetes (T2DM) remission rate and related biochemical indicators;
2. The dyslipidemia of LRYGB patients was significantly improved at 12 months and 36 months, and the low-density lipoprotein and triglyceride levels were significantly reduced at 12 months;
3. LSG is "favored" because of its significantly fewer complications and shorter operation time.
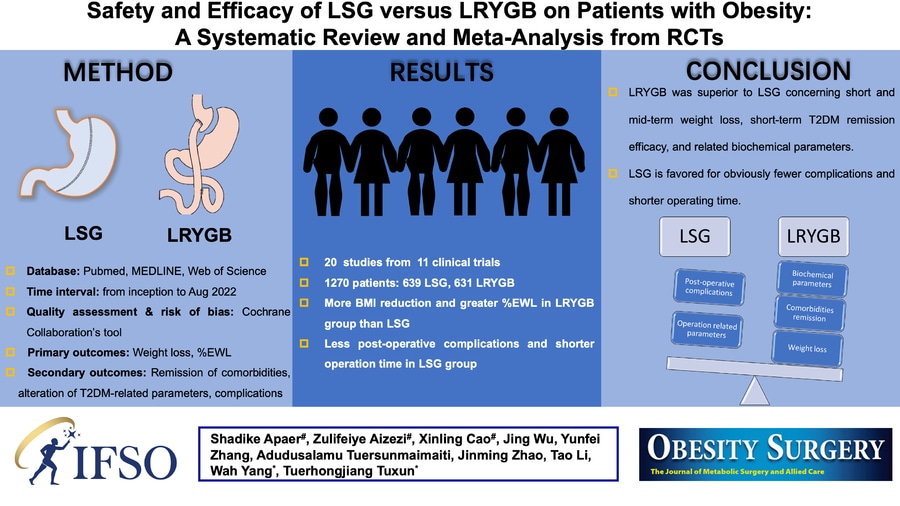
Safety and Efficacy of LSG Versus LRYGB on Patients with Obesity: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis from RCTs
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) are the two most frequently performed techniques in treating obesity and its related comorbidities. We aimed to compare the clinical efficacy and safety of LSG with LRYGB in terms of short- and mid-term outcomes of weight loss, obesity-related comorbidities, and post-operative complications via a meta-analysis of RCTs.
Methods: Clinical comparative RCTs on LSG and LRYGB were searched through PubMed, MEDLINE, and Web of Science databases from inception to August 2022. Pooled outcomes from the selected studies were discussed by the random-effect meta-analysis method. Quality assessment and risk of bias for selected RCTs were implemented, and all the statistical analyses were performed.
Results: Twenty studies, including 1270 patients, were enrolled. Meta-analysis results indicated the great superior efficacy of LRYGB to LSG in BMI loss at 6 (MD -1.35 kg/m2, 95% CI: -2.07 to -0.62, p = 0.0003), 12 months (MD -1.09 kg/m2, 95% CI: -1.86 to -0.33, p = 0.005), and 36 months (MD -1.47 kg/m2, 95% CI: -2.77 to -0.16, p = 0.03) as well as %EWL gaining at 36 months. Significantly higher remission rates of T2DM and dyslipidemia were achieved by LRYGB at 12 months. Besides, better improvements for T2DM-related and lipid biochemical parameters were found favoring LRYGB. However, LSG resulted in a lower post-operative complication rate and shorter operating time.
Conclusions: Present meta-analysis results suggested that LRYGB was superior to LSG concerning short- and mid-term weight loss, short-term T2DM remission efficacy, and related biochemical parameters. LSG is favored for obviously fewer complications and shorter operating time.