#Industry News
Can a ruptured aneurysm be repaired?
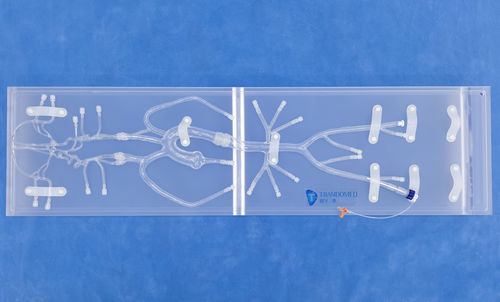
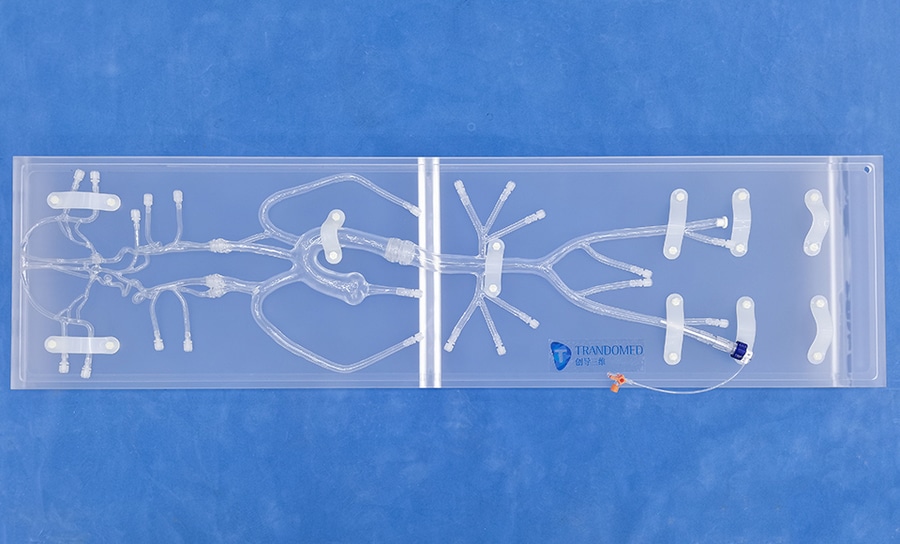
Neuro System Trainer with aneurysm and stenosis
Screening tests and procedures used to diagnose and detect brain aneurysms include:
*CT scan. This specialized X-ray is usually the first test used to detect bleeding in the brain or another type of stroke. The test produces images that are 2D slices of the brain. A CT angiogram can create more-detailed images of the arteries providing blood flow in the brain. The test involves injecting dye that makes it easier to observe blood flow. It also can detect the presence of an aneurysm.
*Lumbar puncture, known as a spinal tap. If you've had a subarachnoid hemorrhage, there will most likely be red blood cells in the fluid surrounding your brain and spine. This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid. If you have symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm but a CT scan doesn't show evidence of bleeding, a test of your cerebrospinal fluid can help make a diagnosis. The procedure to draw cerebrospinal fluid from your back with a needle is called a lumbar puncture.
*MRI. This imaging test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain, either 2D images or 3D images. The images can show if there's bleeding in the brain. A type of MRI that captures images of the arteries in detail is called MR angiography. This type of MRI can detect the size, shape and location of an unruptured aneurysm.
*Cerebral angiogram. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is used. The catheter is inserted into a large artery, usually in the groin or the wrist. The catheter threads past your heart to the arteries in your brain. A special dye injected into the catheter travels to arteries throughout your brain. A series of X-rays can then reveal details about the conditions of your arteries and detect an aneurysm. A cerebral angiogram — also called a cerebral arteriogram — is usually used when other diagnostic tests don't provide enough information.
The use of imaging tests to screen for unruptured brain aneurysms is generally not recommended unless you're at high risk. Talk to your health care provider about the potential benefit of a screening test if you have:
*A family history of brain aneurysms. Particularly if two first-degree relatives — your parents, siblings or children — have had brain aneurysms.
*A disorder that increases your risk of developing a brain aneurysm. These disorders include polycystic kidney disease, coarctation of the aorta or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, among others.
Most aneurysms don't rupture. And for many people, an unruptured aneurysm never causes symptoms. But if the aneurysm ruptures, several factors may affect the outcome, which is known as the prognosis. They include:
*The person's age and health.
*Whether the person has other conditions.
*The size and location of the aneurysm.
*How much bleeding occurred.
*How much time passed before receiving medical care.
About 25% of people who experience a ruptured aneurysm die within 24 hours. Another 25% have complications that lead to death within six months.