#Industry News
Knowledge about Lower Extremity Arteriosclerosis Obliterans
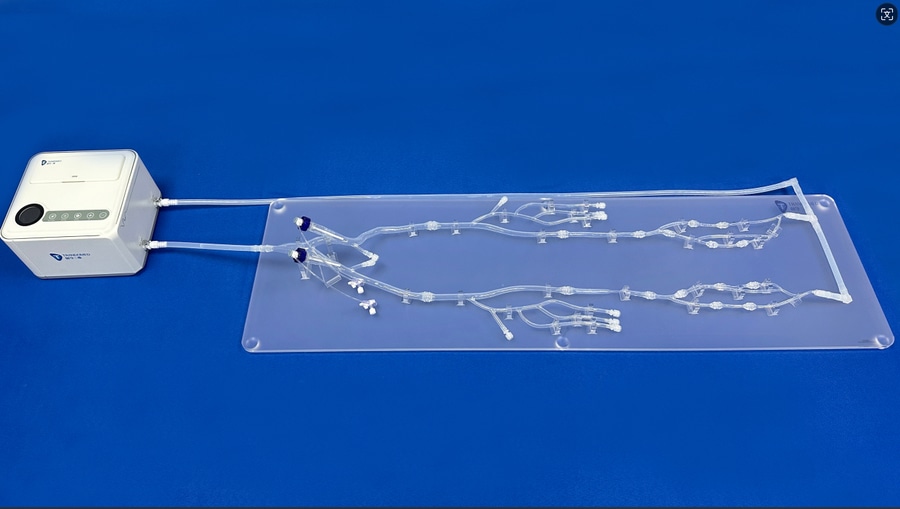
Model: Arterial Leg X (XZD008)
Lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans (LEAS) is a common vascular disease characterized by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries of the lower extremities, leading to arterial stenosis or occlusion and subsequent chronic limb ischemia. Minimally invasive treatments for LEAS include percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with balloon dilation and stent implantation. Traditional surgical options include arterial embolectomy, bypass grafting, and autologous vein bypass.
What is Lower Extremity Arteriosclerosis Obliterans?
Arteriosclerosis is often a systemic vascular disease, and when it affects the arteries of the lower extremities, it can cause limb ischemia. In severe cases, it can lead to ischemic ulcers and gangrene in the lower limbs, commonly known as "leg ischemia" or clinically referred to as lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans.
What are the clinical symptoms of Lower Extremity Arteriosclerosis Obliterans?
Based on the severity of lower limb ischemia, Lower Extremity Arteriosclerosis Obliterans is classified into four stages (Fontaine classification):
1.Mild discomfort stage: Patients may experience decreased skin temperature, sensitivity to cold, mild numbness, fatigue after activity, foot cramps that are difficult to control, thinning of the skin, poor nutrition, reduced hair growth, and increased hair loss.
2.Intermittent claudication stage: When patients walk, the ischemia and hypoxia in the calf muscles can cause spasms, pain, and fatigue. They need to stop and rest until the symptoms improve before they can resume walking. This symptom may recur.
3.Rest pain stage: When the limb ischemia worsens, the compensatory collateral circulation becomes severely insufficient. Ischemic pain occurs in the lower limb muscles and nerves. The most common manifestation is that patients have difficulty sleeping at night, sit with their knees bent, let the lower leg hang down, and cannot raise it, as it worsens the ischemia.
4.Tissue necrosis stage: Tissue necrosis occurs in the ischemic limb, with a significant decrease in skin temperature, the appearance of ulcers at the distal end of the limb, and dark purple necrosis of the toes.
Common surgical options
Common surgical procedures include percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with balloon dilation and stent implantation, vascular bypass grafting, and combined surgical approaches.
The Arterial Leg Model is meticulously crafted, featuring essential components such as the abdominal aorta, iliac artery, femoral artery, superficial femoral artery, deep femoral artery, anterior tibial artery, posterior tibial artery, peroneal artery, and more. These components are securely mounted on an acrylic plate, ensuring stability and precision during simulations.
The model's distinguishing feature lies in its multiple detachable modules, seamlessly connected with customized connectors. This unique design allows for easy interchangeability and customization of individual modules, enabling the simulation of various arterial lesions. With the ability to replicate calcification, chronic total occlusion (CTO), and stenosis, the model accurately replicates the conditions observed in lower extremity arteries.




