#Industry News
In-depth interpretation of T value and Z value in dual-energy X-ray bone densitometer test report
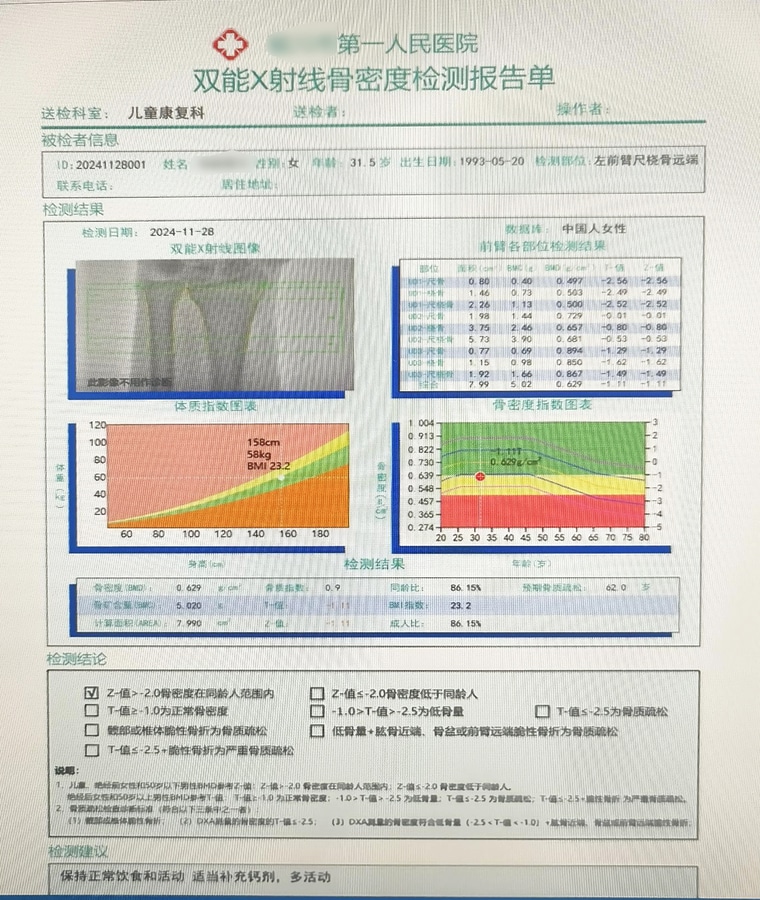
The T-value and Z-value of dual-energy X-ray bone densitometry test report are important indicators for evaluating bone health status, and are of great significance for understanding individual bone status and predicting fracture risk.
In medical diagnostic technology, dual-energy X-ray bone densitometry (DXA), as a high-precision, non-invasive detection method, is widely used to assess bone health, especially for the early screening and diagnosis of osteoporosis. T value and Z value in DXA test report, as the two core indexes to evaluate bone mineral density, are of great significance for understanding individual bone status and predicting fracture risk. In this paper, the meaning of T value and Z value and their application in DXA test report will be analyzed in a simple way.
1. The meaning and application of T value
The T-score, or T-score, is a standardized score from the DXA test that compares a person's bone density with the peak bone density of young, healthy adults of the same sex and race. T-value reflects the bone mineral density of the tested person relative to the same age and gender, and is one of the most significant indicators for the diagnosis of osteoporosis.
• T value ≥-1: indicates normal bone mineral density, and the bone mineral density of the subject is in the normal range compared with young healthy adults of the same sex and race.
• -2.5
T-value ≤-2.5: Usually diagnosed as osteoporosis, the subject's bone density is significantly lower than the average for the same age and gender, and the risk of fracture is significantly increased. At this time, patients need to receive professional treatment, such as medication, physical therapy, etc., to improve bone density and reduce the risk of fracture.
It is important to note that the T-value is not only used for the diagnosis of osteoporosis, but also to evaluate the effect of treatment and monitor disease progression. By regularly detecting changes in the T-value, doctors can adjust the treatment regimen to ensure that patients get the best treatment results.
Second, the meaning and application of Z value
The Z-score, or Z-score, is a standardized score that compares a person's bone density with the average bone density of a healthy person of the same sex, age, and race. The Z-value is mainly used to assess the degree of bone mineral density deviation relative to the peer group, and has special significance for the assessment of bone health in children, adolescents and older adults.
A Z-value of -2 to +2 indicates that the subject's bone density is near the average for the age group, and there are no significant signs of bone loss.
Z-value <-2: indicates that the subject's bone mineral density is lower than the average level of the age group, and there is a risk of bone loss. In children and adolescents, abnormal Z-values can indicate growth delays or bone disease. In adults, it may be associated with secondary osteoporosis or other bone diseases.
Abnormal increase in Z value: Although less common than a decrease in Z value, it may also indicate certain special conditions, such as skeletal sclerosis.
The application of the Z-value is not limited to the diagnosis of osteoporosis, but is also used to assess the cause of bone diseases, predict the risk of fracture, and monitor the effect of treatment. By comparing the Z-value changes at different time points, doctors can understand the changing trend of bone health status of the subject and develop personalized treatment and management plans.
Third, the comprehensive application of T value and Z value
In DXA test reports, T-values and Z-values are often used in combination to provide a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of bone health. T-value is mainly used to diagnose osteoporosis and evaluate the treatment effect, while Z-value is used to evaluate the bone mineral density deviation of the tested subjects relative to the age group, which provides an important reference for etiological analysis and treatment plan formulation.
The T-value and Z-value of dual-energy X-ray bone densitometry test report are important indicators for evaluating bone health status, and are of great significance for understanding individual bone status and predicting fracture risk. By regularly detecting changes in T and Z values, we can detect bone health problems in time and take necessary preventive measures and treatments to protect bone health and improve quality of life.