#Industry News
Future Trends and Innovations in Dental Instruments
This article briefly explores the future trends in dental instruments, focusing on digitalization, personalization, minimally invasive techniques, and sustainability, and how these innovations will enhance treatment outcomes and patient experience.
With the rapid advancement of technology, the field of dentistry is undergoing unprecedented transformations. The dental instruments of the future will be smarter, more personalized, and geared towards sustainability and eco-friendliness. This article explores the key trends and innovations in the dental instrument industry and how these changes will impact future dental practices and patient experiences.
The Proliferation of Digitalization and Intelligence
Digital technology has brought revolutionary changes to many industries, and dentistry is no exception. Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology is transforming the process of creating dental restorations. These technologies allow dentists to fabricate precise crowns, bridges, and implants directly in the clinic, significantly reducing patient wait times and increasing treatment efficiency and accuracy. Concurrently, 3D printing technology is on the rise. With 3D printing, dental models, orthodontic devices, and even some restorations can be directly printed, accelerating the production process and offering highly personalized treatment plans.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also rapidly integrating into dental diagnostic processes. AI systems can analyze dental images, helping dentists identify cavities, periodontal disease, and other oral conditions. AI not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also provides optimized treatment suggestions through big data analysis, further improving patient outcomes.
Minimally Invasive Technology and Enhanced Patient Comfort
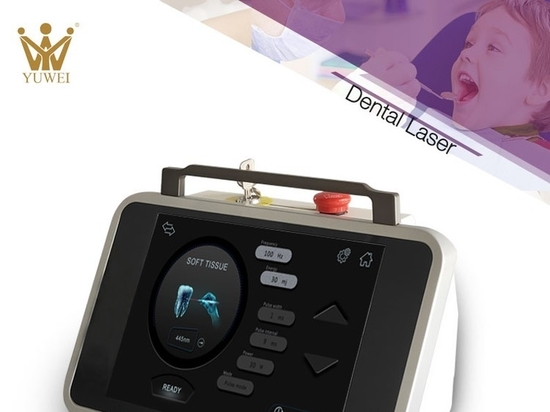
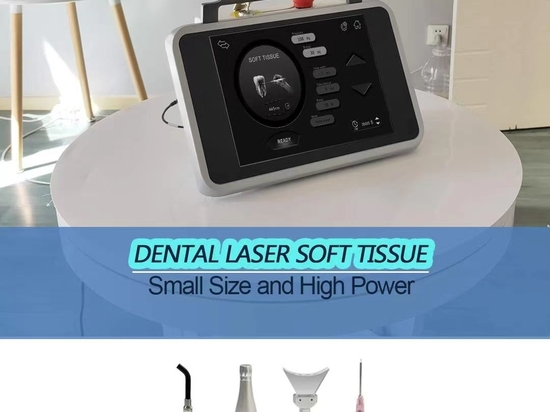
Future dental technologies will focus more on patient comfort and experience. For instance, the widespread application of laser technology is revolutionizing dental surgery. Lasers can precisely cut tissue, remove cavities, and treat periodontal disease, all with minimal discomfort for the patient. Additionally, laser technology has the advantage of reducing bleeding and speeding up recovery times, significantly shortening the post-operative recovery period.
The advent of needle-free injectors is another notable innovation. These devices deliver anesthesia through high-pressure air, avoiding the pain and fear associated with traditional needles. This technology not only improves patient experience but also reduces stress for dentists during procedures.
Personalization and Precision in Treatment
With advancements in genomics, personalized medicine is also gaining traction in the field of dentistry. In the future, dental treatments will be customized based on the patient's genetic information, offering more precise treatment plans. This means that dentists can predict how patients will respond to specific treatments based on their genetic characteristics and develop more appropriate treatment plans.
The development of personalized orthodontic devices also reflects the trend towards personalized treatment. For example, the widespread use of clear aligners allows patients to enjoy aesthetic appeal while undergoing orthodontic treatment, with devices tailored to the specific shape of their teeth for a more comfortable wearing experience.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
As global environmental awareness rises, the dental field is also beginning to focus on sustainable development. Future dental instruments and materials will increasingly use eco-friendly and biodegradable materials, reducing the environmental impact. This not only lowers the carbon footprint of clinics but also reduces the health risks for patients exposed to harmful chemicals.
Moreover, energy-efficient dental equipment, such as LED lights and water-saving devices, is gradually becoming the preferred choice for clinics. These devices not only reduce energy consumption and costs but also align with global trends in energy conservation and emissions reduction.
The Rise of Remote Dental Care
Telemedicine has seen significant development in recent years, and dental care is finding its place in this trend. Remote consultation services allow patients to consult with dentists from home via video calls, receiving preliminary diagnoses and treatment recommendations, especially important in remote areas or during pandemics. Meanwhile, the emergence of smart oral health monitoring devices enables patients to monitor their oral health in real-time at home and share data with their dentists for remote monitoring and guidance.
Applications of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality technologies are also expanding their applications in the dental field. These technologies are used not only in dental education and training but also help dentists perform more precise procedures during treatment. For instance, students can simulate complex surgical processes through VR to improve their skill levels, while patients can better understand their treatment process through these technologies, enhancing their understanding and trust in treatment plans.
Data Security and Privacy Protection
As digitalization increases, the security and privacy of patient data become important issues. Future innovations will include more robust encryption technologies and privacy protection measures to ensure the safety of patient information during transmission and storage.
In conclusion, the development of dental instruments in the future will be characterized by trends towards intelligence, personalization, sustainability, and remote care. These innovations not only improve the efficiency and effectiveness of treatments but also significantly enhance the overall patient experience. With the continuous advancement of technology, the field of dentistry will see more revolutionary changes, further promoting the improvement of global oral health standards.