#Industry News
Effectiveness of Diode Lasers in Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
Diode lasers demonstrate high efficiency and safety in tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy procedures. By providing precise cutting and hemostasis, diode lasers reduce postoperative bleeding and recovery time, offering a better treatment experience for patients.
With advancements in medical technology, laser applications in surgical procedures have become increasingly widespread. Among these, diode lasers have gained significant attention in ENT surgeries, especially in tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, due to their unique optical properties and high tissue absorption rates.
1. Basic Principles of Diode Lasers
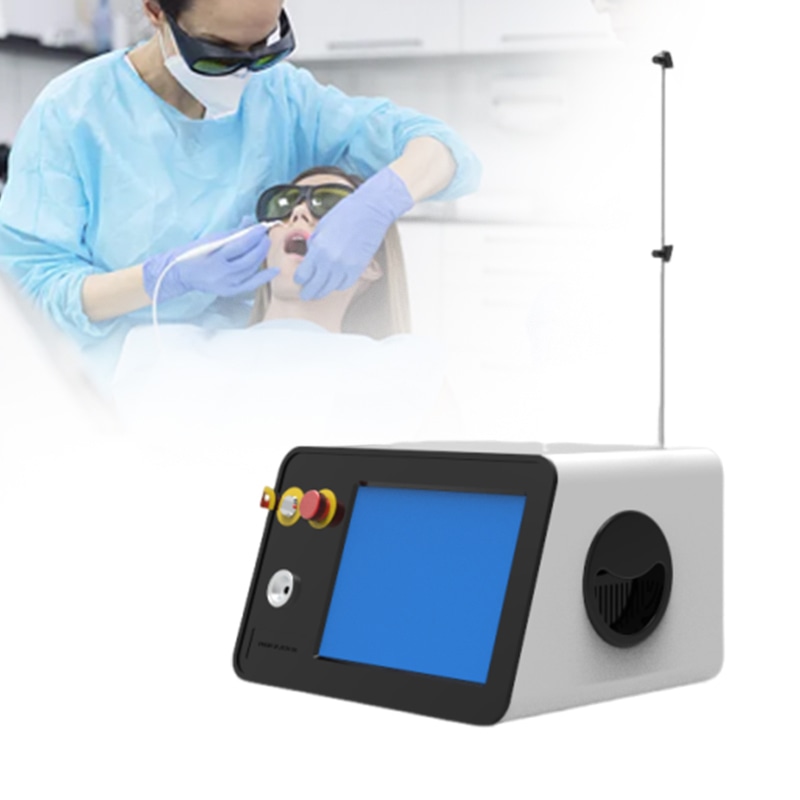
Diode lasers are semiconductor-based lasers, typically operating in the wavelength range of 800-980 nm. This wavelength is highly absorbable by water and hemoglobin in soft tissues, enabling efficient cutting and coagulation. Furthermore, diode lasers are compact, energy-efficient, and easily integrated into surgical instruments, making them ideal for operating room settings.
2. Applications in Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a common ENT surgery performed to treat chronic tonsillitis or hypertrophy. Traditional surgical methods, such as scalpels or electrocautery, often lead to significant bleeding and postoperative pain. Using diode lasers for tonsillectomy addresses these issues effectively:
Reduced Bleeding: Diode lasers coagulate blood vessels while cutting, minimizing intraoperative and postoperative bleeding risks.
Less Postoperative Pain: By limiting thermal damage to surrounding tissues, lasers reduce postoperative discomfort.
Faster Recovery: Patients experience quicker wound healing and reduced recovery times.
3. Applications in Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is commonly performed to treat adenoid hypertrophy causing airway obstruction or recurrent infections. Diode lasers offer similar advantages in this surgery:
Precision: The high energy density of diode lasers enables precise tissue removal, protecting healthy tissue.
Reduced Infection Risk: The laser's sterilizing effect helps decrease postoperative infection chances.
Flexible Operation: Compact laser devices are maneuverable, making them ideal for complex anatomical areas.
4. Clinical Studies and Outcomes
Studies show that patients undergoing diode laser tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy experience a 50% reduction in intraoperative bleeding and significantly lower postoperative complications. Pain scores reported by patients are 20%-30% lower than traditional methods. Additionally, surgeons note clearer surgical fields and easier operation using lasers.
5. Future Outlook
While diode lasers are well-established in ENT surgeries, there is room for improvement. Future research may focus on optimizing laser parameters, increasing cutting efficiency, and developing smarter surgical aids to enhance safety and outcomes.
Conclusion
Diode laser technology has proven to be highly effective and safe in tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy procedures. By reducing bleeding, minimizing pain, and shortening recovery times, diode lasers provide an enhanced treatment experience for patients and a more efficient tool for surgeons. This technology holds promise for broader medical applications in the future.