#Industry News
Study on the effects of excessive cortisone
metabolic rate of male and female C57BL/6J mice
Study Introduction
Glucocorticoids are crucial for regulating metabolic processes and have significant applications in medical treatments. However, excessive glucocorticoids are known to cause negative metabolic effects, including hyperglycemia, muscle atrophy, and fat accumulation, ultimately leading to Cushing's syndrome. The effects of glucocorticoids on energy metabolism and metabolic rate remain unclear and warrant investigation in male and female mice.
Research Methods
A total of 24 male and 24 female C57BL/6J mice were randomly assigned to either the cortisone group (100 mg/L, approximately 300 μg/day) or the vehicle control group. The mice had free access to drinking water and were fed a standard diet for three weeks. In the last week of treatment, the mice were placed in an animal energy metabolism system for indirect calorimetry assessment.
Research Results
After cortisone intervention, typical phenotypes of glucocorticoid excess were observed. However, compared to male mice, female mice exhibited significantly greater fat accumulation and weight gain. During the day, female mice receiving cortisone treatment showed increased energy expenditure (EE, 25 ± 5.9%), oxygen consumption (21.7 ± 10.0%), and carbon dioxide production (36.4 ± 14.3%) compared to the control group, while males did not show similar increases. However, cortisone did significantly elevate the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) to 1 in both male (10.7 ± 5.7%) and female mice (11.8 ± 7.0%).
In the evening, when the mice were naturally more active and energy efficiency increased, energy efficiency, oxygen consumption, and carbon dioxide production in female cortisone mice no longer showed increases compared to the control group. Nevertheless, female mice maintained a higher RER (7.6 ± 4.8%), while the RER in male mice was moderately elevated (3.2 ± 2.6%), with both remaining close to or exceeding 1. Mice receiving cortisone treatment exhibited persistent hyperphagia and polydipsia, consuming significantly more food than the control group during both night and day, with intake peaking at night. Subsequent metabolomic analysis of tissue samples (skeletal muscle, liver, and gonadal fat) revealed significant treatment and gender differences.
Research Conclusions
These findings provide further insights into the metabolic consequences of glucocorticoid excess in male and female mice. While energy metabolism and metabolic rates change in both sexes (particularly during the day), the impact of glucocorticoid excess on the metabolism of female mice may be more pronounced. Researchers can further investigate whether these changes are solely due to increased animal activity, enhanced feeding and drinking, or other mechanisms. Additionally, further experiments can determine whether 11β-HSD1 knockout (KO) can prevent these changes, as it does for other negative metabolic effects associated with glucocorticoid excess, thereby advancing the development of new drugs.
Relevant Instrument Solutions Provided by Tow-Int Tech
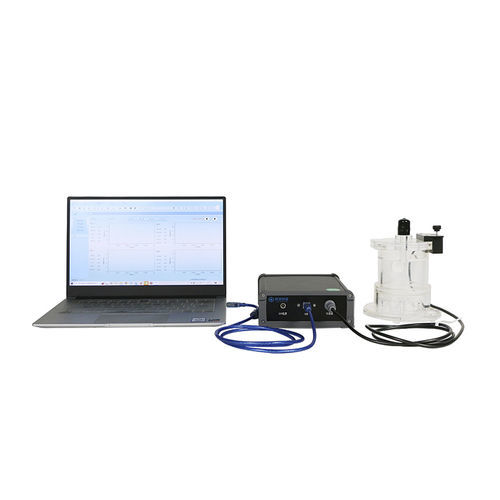
Animal Energy Metabolism Monitoring System
The animal metabolism monitoring system developed by Tow-Int Tech is a highly flexible modular platform. One software can simultaneously control different functional modules within the breeding cage, including:
Respiratory entropy metabolism monitoring module
Environmental temperature control module
Feeding, drinking andweight monitoring module
Urine/feces monitoring module
Autonomous activity and training module
Learning and memory monitoring module
Physiological telemetry monitoring module
Features
It can accurately measure oxygen consumption, CO2 production, respiratory metabolism rate, and more.
It is equipped with 4/8/16 channels, each with an independent controller, allowing for standalone use and flexible expansion, plug-and-play (the chamber can be customized according to experimental needs).
Airflow drying function:The airflow drying feature ensures that the gas composition of samples is not affected by humidity and other adsorptive materials, guaranteeing the accuracy of gas measurement data.
Digital flow valve:Controls gas flow with an accuracy of 0.01 L/min.
Reference gas detection:Can monitor the O2 and CO2 content in the ambient air of the experimental environment.
Carbon dioxide measurement:Measurement range: 0-10,000 ppm, measurement resolution ≤ 0.0001%.
Oxygen measurement:Resolution 0.0001%, measurement range: 0.1-25%.
Data acquisition and analysis system (software):Includes an integrated data collector and software that connects to a computer via USB. The data is displayed in an integrated manner, providing trend curves for various indicators.
Animal Expiratory Acquisition System
The Animal Expiratory Acquisition System is a simplified version of the Animal Metabolism Monitoring System (HOME CAGES). It is primarily used to monitor the animals' oxygen consumption, CO2 production, respiratory metabolism rate, and other metrics, serving as a standard device for measuring animal energy metabolism.
Animal Metabolism Monitoring System
The Animal Metabolism Monitoring System is a comprehensive system for monitoring animal metabolic indicators. It can real-time monitor food intake, water consumption, and activity levels, with optional features for measuring oxygen consumption, CO2 production, respiratory metabolism rate, and more. The system enables the separation and collection of animal feces and urine. It also allows for real-time monitoring of feces and urine weight to analyze the animal's metabolic status. The Animal Metabolism Monitoring System mainly consists of a data acquisition and controller, metabolic cages, an environmental chamber, a computer, and software.
The animal metabolic cage and fecal/urine collection tube are made of high-gloss PSU material, effectively preventing the sticking and residue of animal feces and urine.
The drinking water and feeding troughs can be easily removed, allowing for the addition of feed and water without interrupting the experiment and minimizing disturbance to the animals.
The design includes a liquid leakage recovery system for the drinking water, enhancing the accuracy of drinking measurement and avoiding any impact on urine collection.
The system features a modular design, allowing functions to be flexibly added or removed as needed.
It also has independent controllers with a flexible number of channels that can be expanded as required. Additionally, it includes a refrigeration module for the feces and urine collector, enabling frozen storage.
Contact us now!
We are committed to making your research easier, more accurate, and more efficient and helping you build confidence in your data! We have provided services for a large number of customers, giving us rich experiences in offering customized, professional solutions according to your needs.