#Industry News
Heavy review! A panoramic view of obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, complications and management strategies
shenyun medical
Obesity, a global health challenge, is spreading at an alarming rate. However, behind it are complex biological, genetic, environmental and socioeconomic factors. The paper is a collaboration of a team of experts from multiple fields in China, which integrates a large number of literatures and deeply analyzes the epidemiology, pathophysiological mechanisms, related complications, etiological risk factors and management and treatment strategies of obesity. It also emphasizes the multidimensional perspective of the complex relationship between obesity and health outcomes, draws a panoramic view of the current obesity research field, and provides an interdisciplinary and multidimensional perspective on the complex relationship between obesity and health. The paper was published in the international journal The Innovation Medicine.
Obesity, a global health challenge, is spreading at an alarming rate. However, behind it are complex biological, genetic, environmental and socioeconomic factors. The paper is a collaboration of a team of experts from multiple fields in China, which integrates a large number of literatures and deeply analyzes the epidemiology, pathophysiological mechanisms, related complications, etiological risk factors and management and treatment strategies of obesity. It also emphasizes the multi-dimensional perspective of the complex relationship between obesity and health outcomes, draws a panoramic view of the current field of obesity research, and provides an interdisciplinary and multi-dimensional perspective on the complex relationship between obesity and health. The paper was published in the international journal The Innovation Medicine.
Interpretation of the cover of this issue of The Innovation Medicine:
Reverse obesity and enjoy health! Obesity has become a global health crisis. The cover of this issue uses a sharp contrast between the image of obese and healthy people to intuitively show a series of serious health problems that obesity may cause, such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular system, respiratory system, endocrine and reproductive system diseases, cancer and intestinal flora disorders. These problems not only affect the quality of life of individuals, but may also lead to serious health crises. The cover emphasizes the importance of a healthy lifestyle. Through effective interventions and treatments, such as lifestyle adjustments, medications and surgical treatments, obesity can be effectively controlled and improved. The emergence of digital technology and wearable devices promotes more informed decision-making and personalized feedback. The cover of this issue provides readers with a comprehensive and profound perspective on the problem of obesity.
Obesity has become a global, preventable health crisis that affects multiple organ systems and is associated with a variety of diseases. This health crisis requires a concerted, multidisciplinary effort to effectively address its causes and consequences. Successful prevention and treatment of obesity relies on the concerted efforts of medical experts, nutritionists, biologists, psychologists, policymakers, and society at large.
Advances in molecular technologies and multi-omics approaches have provided a deeper understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms of obesity. Obesity research must continue to evolve with a focus on personalized treatment strategies. Genetic and genomic studies can provide insights into individual susceptibility to obesity and guide the development of targeted pharmacological interventions. Lifestyle intervention is the first choice for weight control because of its low cost. In addition, the effectiveness and safety of pharmacological treatments and bariatric surgery have been thoroughly evaluated.
With the advancement of mobile technology and the use of wearable devices, these emerging tools can provide real-time feedback on dietary intake and physical activity, promote behavioral changes, and support long-term weight maintenance. The emergence of digital technologies and wearable devices offers an exciting frontier in obesity management, facilitating more informed decisions and personalized feedback. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can further refine these approaches, providing predictive analysis and early warning signs of weight gain or related health complications.
The role of public health policy in obesity management cannot be overemphasized. Policymakers should promote healthy choices by regulating the food industry, promoting exercise and nutrition education. This includes effective food labelling, limiting the marketing of unhealthy foods to children, and supporting community initiatives for fresh produce and safe exercise spaces. In 2022, the UK government requires calorie labelling on menus in restaurants, cafes and takeaways to help reduce calorie intake. Similarly, Singapore has introduced a beverage nutrition labelling system that classifies high-sugar drinks according to their sugar and saturated fat content to reduce their consumption.
The future of obesity research and treatment is promising but also challenging. A multidisciplinary approach is essential to address obesity, bringing together different expertise to develop integrated treatment strategies. By adopting innovative technologies and fostering a culture of collaboration, we can work towards a future where obesity is effectively managed and its social burden is significantly reduced.
Graphical Abstract
Figure 1: Global trends in overweight/obesity, deaths due to overweight/obesity, and disability-adjusted life years.
(A) Number of adults and adolescents with overweight/obesity, 2020-2035 (100 million). (B) Prevalence of overweight/obesity in adults and adolescents, 2020-2035 (%). (C) Proportion of deaths and disability-adjusted life years due to overweight/obesity, 1990-2019.
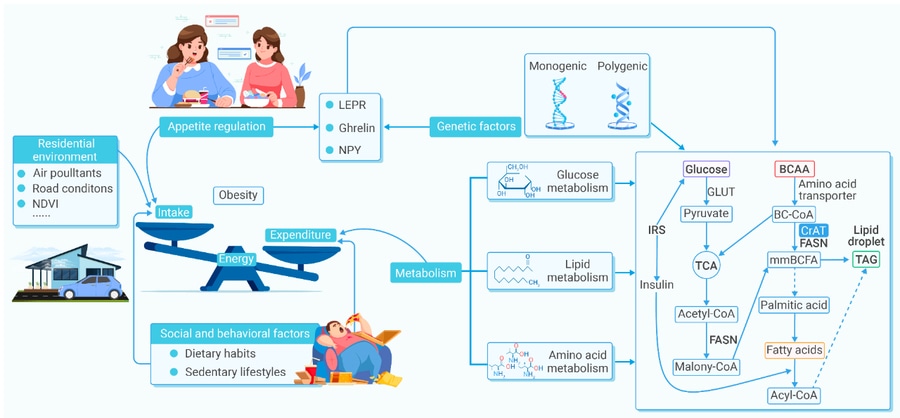
Figure 2: Obesity is a multifactorial disease influenced by genetic and environmental factors. The heritability of obesity may be due to single gene mutations or polygenic variants. Genetic regulation of appetite significantly affects energy intake, and genetic abnormalities can disrupt metabolic pathways, thereby affecting the metabolism of glucose, lipids, and amino acids. As energy intake exceeds energy expenditure, living environment and sedentary lifestyle lead to increased obesity rates.
Figure 3: Obesity-related diseases affect multiple systems in the human body.
Figure 4: Effects of obesity on respiratory physiology Increased body mass index can lead to a decrease in lung capacity. Adipose tissue surrounding the upper airway can lead to upper airway stenosis and collapse. Tissue surrounding the abdomen and chest wall can lead to ventilation-perfusion mismatch and hypoxia. The ventilation drive of obese patients compensates for the work of breathing and low respiratory efficiency. In patients with OHS, the failure of this mechanism and the decline in central drive will lead to hypercapnia and hypoxemia.
Figure 5: Obesity is a major risk factor for cancer and immune diseases Obesity affects the number and function of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment, promoting immune diseases and tumor growth.
Figure 6: In the context of obesity treatment, dietary intervention, prebiotics, probiotic supplementation, fecal microbiota transplantation, anti-obesity drugs and bariatric surgery all play different degrees of microbial regulation, ultimately contributing to weight management.
Figure 7: Illustration of obesity intervention and treatment. * Specific medication should be based on actual clinical conditions.