#Product Trends
Enhancing Treatment Strategies with Aorta Models
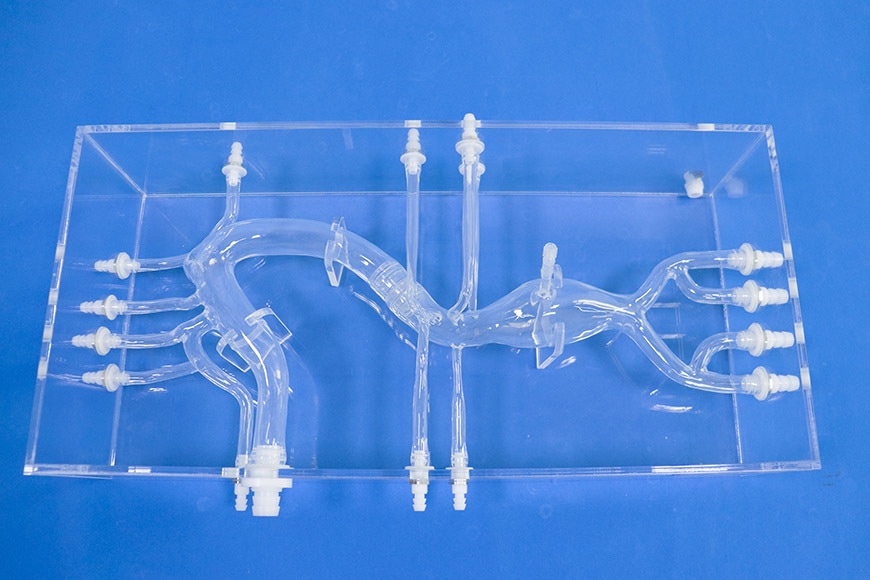
Aorta Model With AAA (fixed in acrylic box)
Introduction
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a significant healthcare concern characterized by the localized dilation or bulging of the abdominal aorta. It poses a potential risk of rupture, leading to life-threatening consequences. The treatment of AAA requires precise planning and expertise. With the advancements in medical technology, the development of Aorta Models with abdominal aortic aneurysm using 3D printing techniques has revolutionized the field of vascular surgery and interventions. In this article, we explore the significance and benefits of these models in improving patient outcomes.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm refers to the abnormal enlargement of the abdominal segment of the aorta, the main blood vessel supplying oxygenated blood to the lower part of the body. If left untreated, AAA can lead to the rupturing of the weakened arterial wall, causing severe internal bleeding and potentially fatal complications. Early detection and appropriate treatment are essential to mitigate the risks associated with AAA.
Aorta Model with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Aorta models with abdominal aortic aneurysm are 3D printed replicas of the actual patient's aorta, created using real computed tomography (CT) data. These models ensure physiological fidelity by accurately reproducing the patient's specific anatomical characteristics, including the full aorta down to the femoral artery, with emphasis on the abdominal aortic aneurysm itself.
Significance and Benefits of Aorta Models with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
a) Treatment Planning: Aorta models provide clinicians with a tangible and comprehensive representation of the patient's specific AAA condition, enabling detailed preoperative planning. Surgeons can assess the anatomy, location, and dimensions of the aneurysm, facilitating the selection of the appropriate treatment strategy for each patient.
b) Simulation and Education: These 3D printed models offer a valuable platform for simulation and education. Surgeons and trainees can practice various treatment techniques, such as endovascular repair or open surgical approaches, on the anatomically accurate models. This allows for hands-on training and skill development in a risk-free environment.
c) Patient Education: Aorta models contribute to patient education and informed decision-making. The visual representation of the AAA helps patients better understand their condition, the treatment options available, and the potential benefits and risks associated with each approach. This promotes shared decision-making and empowers patients to actively participate in their own healthcare journey.
d) Device Selection and Testing: Aorta models with abdominal aortic aneurysm facilitate the evaluation and testing of different devices used in AAA treatment, including stent grafts and endovascular tools. The models allow surgeons and researchers to assess the compatibility, appropriateness, and effectiveness of these devices in a patient-specific context.
e) Research and Innovation: Aorta models contribute to ongoing research and innovation in the field of vascular interventions. By replicating patient-specific AAA anatomies and simulating treatment scenarios, researchers can study the biomechanical factors associated with aneurysm progression, develop novel treatment approaches, and improve device design for better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The use of Aorta Models with abdominal aortic aneurysm, created through 3D printing based on real CT data, offers significant advantages in the treatment, planning, education, and research related to AAA. These models provide a realistic representation of the patient's anatomy and support the development of personalized treatment strategies. With continued advancements in 3D printing technology, these models have the potential to enhance patient outcomes and drive innovation in the field of vascular surgery.





