#Industry News
Tow-Int Tech's WBP System Supports Research
on the Prevention and Treatment of Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Introduction
Recently, Chen-Xiao Yan from Nanjing University, along with researchers Kena Sun, Xia Zhu, and others, investigated the mechanism by which oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) alleviate acute lung injury (ALI) via the gut-lung axis, by inhibiting the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and inflammation. The article was published in the Journal of Functional Foods. This journal focuses on research related to functional foods and covers various fields, including food science, nutrition, and biology, making it a prominent academic publication in this area.
Research Background:ALI and Sepsis
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition characterized by multi-organ dysfunction, with the lungs being one of the primary organs affected. Over 50% of sepsis patients develop acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which significantly impacts patient prognosis.
Role of OPCs:
Oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) are a class of natural polyphenolic compounds extracted from plants. They possess various bioactivities, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Experimental Methods
Animal Model:
Rats were used as experimental subjects to investigate the effects of oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) by administering grape seed extract.
Intervention:
OPCs were administered orally, with samples collected at various time points for analysis.
Detection Indicators:
Intestinal Barrier Function:The effects of OPCs on the thickness of the intestinal mucus layer, intestinal permeability, and gut microbiota composition were assessed.
Pulmonary Pathological Changes:Lung tissue structure and cell apoptosis were observed using tissue section staining and immunofluorescence microscopy.
NETs Formation:Plasma and lung tissue levels of cf-DNA, NE (neutrophil elastase), and H3cit (citrullinated histone H3) were measured to assess NETs formation.
Inflammatory Markers:The concentrations of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in plasma and lung tissue were measured.
Experimental Results (Improvement of Acute Lung Injury in Sepsis Mice by OPCs)
Enhancement of Intestinal Barrier Function:OPCs promoted mucus secretion, increased REG3γ expression, and strengthened the intestinal mucus barrier, preventing intestinal bacterial translocation.
Regulation of Gut Microbiota:OPCs inhibited the proliferation of harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Shigella, while increasing the number of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus, maintaining gut microbiota balance.
Reduction of Pulmonary Damage:OPCs significantly reduced the apoptosis rate in lung tissues and NETs formation, lowered the levels of inflammatory cytokines, and alleviated sepsis-induced lung injury.
Impact on Metabolic Pathways:Preliminary results indicated that OPCs may exert protective effects by altering gut microbiota-related metabolic products, although further research is needed to clarify the specific mechanisms.
Increased Survival Rate and Improved Pulmonary Function:Sepsis mice were injected with varying concentrations of OPCs, and a dose of 60 mg/kg significantly increased the survival rate. Compared to the LPS group, the OPC-pretreated mice showed reduced lung hemorrhage and swelling, and improved lung function, reflected in a shorter relaxation time and increased mid-expiratory flow, indicating that OPCs can alleviate lung injury.
Anti-inflammatory Effects:
OPCs reduced the levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in plasma and lung tissue, inhibited the LPS-induced increase of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), and restored the balance between tissue factor (TF) and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), thereby alleviating lung inflammation and damage.
Discussion and Conclusion
OPCs exert significant protective effects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury by regulating the gut-lung axis. This includes enhancing intestinal barrier function, regulating gut microbiota homeostasis, and inhibiting pulmonary NETs formation and inflammation. The study provides theoretical support for the use of OPCs in clinical treatment of sepsis-related acute lung injury. However, further research is needed to explore the mechanisms involved in metabolic pathways to facilitate clinical applications and the development of functional plant-based products.
During the experiment, the researchers used the Tow-Int Tech whole-body plethysmography system to study lung function in mice.
1. Measurement Principle and Equipment:
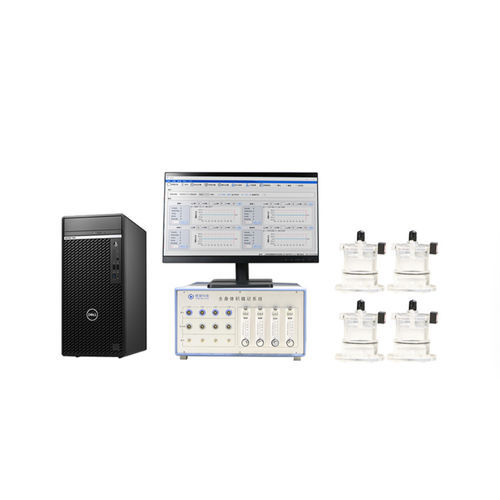
This technique measures lung function by detecting pressure changes within a volume chamber caused by animal respiratory movements. The experiment used Tow-Int Tech’s 8-channel whole-body plethysmography system (WBP-8M), with a respiratory sensor to record pressure variations.
2. Experimental Procedure:
a. First, the mice labeled with bitter acid were placed in the Tow-Int Tech whole-body plethysmograph for a two-minute acclimation period.
b. Then, the mice’s breathing was continuously monitored for eight minutes, during which the Tow-Int Tech whole-body plethysmography system recorded the pressure changes related to respiration.
3. Data Analysis and Results:
The data were analyzed using the Tow-Int Tech plethysmograph analysis software algorithm, which derived the mice's lung function parameters from the recorded pressure change data. These parameters reflect the status of lung function in the mice and provide foundational data for subsequent studies on the effects of OPCs on lung function. This data supports a deeper understanding of the mechanisms by which OPCs improve lung function in sepsis-induced mice.
Tow-Int Tech Whole-Body Plethysmography System
The Tow-Int Tech whole-body plethysmography system employs the unrestrained whole-body plethysmography method to conduct lung function and airway responsiveness tests on awake and freely moving small animals. Animal respiration causes the thoracic movement inside the plethysmograph chamber, leading to changes in volume. These volume changes are converted into electrical signals through pressure transducers and amplifiers, then processed by a computer to present the breathing curve and calculate various respiratory parameters, such as tidal volume (TV), peak expiratory flow (PEF), and respiratory frequency.
In combination with optogenetics, this approach can explore the control mechanisms of respiratory rhythm.
Oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs) are a class of polyphenolic compounds that are widely found in various plant-based foods in nature. These substances are a form of proanthocyanidins, typically existing in oligomeric forms, such as dimers, trimers, and so on. Foods rich in oligomeric proanthocyanidins include, but are not limited to:
Grape Seeds: Grape seeds are one of the most well-known sources of oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs).
Cranberries: These small red berries also contain relatively high concentrations of OPCs.
Cocoa Beans: The raw material for chocolate contains a certain amount of OPCs.
Apple Skins: Particularly the skins of red and green apple varieties.
Black Goji Berries: Considered a high-quality source of proanthocyanidins.
Pomegranate: Both pomegranate juice and its peel are excellent sources of OPCs.
Red Wine: Due to the use of grape skins and seeds during the winemaking process, red wine is also a source of OPCs.
In addition to the foods mentioned above, other fruits such as blueberries, blackberries, and strawberries, as well as certain nuts and seeds, may also contain OPCs. It's important to note that processing methods can affect the concentration and bioavailability of these compounds. For example, excessive heating or prolonged storage can reduce the levels of active ingredients. To achieve the best results, it is recommended to consume fresh or properly processed products that preserve their nutritional content.
Contact us now!
We are committed to making your research easier, more accurate, and more efficient and helping you build confidence in your data! We have provided services for a large number of customers, giving us rich experiences in offering customized, professional solutions according to your needs.