#Industry News
Electroacupuncture treatment successfully alleviates COPD symptoms in experimental rat models
showing potential as an adjunctive therapy for COPD in the future
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide, and current pharmacological treatments are associated with side effects. Recently, researchers Lu Liu, Zili Tang, and colleagues published a study titled "Transcriptomic Insights into Different Stimulation Intensity of Electroacupuncture in Treating COPD in Rat Models" in the Journal of Inflammation Research.
This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms of electroacupuncture at 1mA and 3mA intensities on COPD in rat models. Through model establishment, treatment grouping, multi-parameter detection, and omics analysis, the researchers found that both intensities improved lung function, but gene expression patterns varied. They identified eight candidate genes and related pathways, providing new targets and insights for the electroacupuncture treatment of COPD.
1. Research Background
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by chronic inflammation, alveolar destruction, and small airway obstruction, ranking as the third leading cause of death globally. Current pharmacological treatments are associated with side effects, while electroacupuncture (EA) has demonstrated some efficacy in clinical treatment. However, stimulation intensity remains unstandardized. This study aimed to compare the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of 1mA and 3mA electroacupuncture on COPD in rat models and to reveal the molecular regulatory mechanisms through transcriptomic analysis.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1 Experimental Animals and Grouping
Animal Selection: Male Sprague-Dawley rats aged 12–14 weeks.
Animal Grouping: Rats were randomly divided into four groups, each consisting of six animals: normal control group (NC), COPD group, COPD+1mA-EA group (EA-1mA), and COPD+3mA-EA group (EA-3mA).
2.2 COPD Model Establishment and Electroacupuncture Treatment
Model Establishment: The COPD model was induced using a combination of passive smoking (CS) and intratracheal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Rats were exposed to cigarette smoke in a whole-body exposure system for 2 hours daily over 12 weeks, with LPS injections administered on days 1, 31, and 61.
Electroacupuncture Treatment: Starting on day 77, EA was performed on rats in the EA-1mA and EA-3mA groups for 20 minutes daily over two weeks. Acupoints BL13 (Feishu) and ST36 (Zusanli) were selected, with needle insertion depths of 6mm and 7mm, respectively. Sparse-dense waves with a frequency of 4/20Hz and intensities of 1mA and 3mA were applied. Rats in the NC and COPD groups underwent anesthesia without EA.
2.3 Evaluation Indicators
Lung Function Assessment: Lung function parameters, including forced expiratory volume (FEV), forced vital capacity (FVC), and FEV/FVC ratio, were measured using a pulmonary function testing system for experimental animals.
Histopathological Examination: Lung tissue morphology was assessed using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, and inflammation infiltration was detected via immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining. The alveolar surface area to interstitial area ratio (A/S) and the mean optical density (IOD/area) of macrophages and T lymphocytes were calculated.
Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Indicators: Serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Biochemical kits were used to measure superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels in serum and lung tissue.
Transcriptomic Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and Analysis: Total RNA was extracted from lung tissue for RNA-Seq analysis to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were performed. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was used to construct gene co-expression networks and determine the relationship between modules and traits.
Validation by RT-qPCR and Western Blot (WB): Selected DEGs were validated at the mRNA and protein levels using RT-qPCR and WB, respectively.
2.4 Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and analyzed using Prism 9.0 software. For data with normal distribution and homogeneity of variance, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used, followed by least significant difference (LSD) t-tests for pairwise comparisons. For non-normally distributed data, the Kruskal-Wallis test was applied. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Experimental Results
3.1 Effects of Electroacupuncture on Lung Function, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in COPD Rats
Improvement in Lung Function: Compared with the NC group, the FEV/FVC ratio in the COPD group was significantly reduced, indicating severe airflow limitation. Both EA-1mA and EA-3mA treatments significantly improved the ratio, though no significant difference was observed between the two EA groups.
Histopathological Changes:
HE staining showed thickened alveolar septa, emphysema formation, and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the COPD group. The A/S ratio was reduced, and the number of inflammatory cells increased. EA-3mA treatment significantly increased the A/S ratio, while EA-1mA also showed an increasing trend, although it did not reach statistical significance. Both treatments inhibited local aggregation of inflammatory cells. IHC staining results were consistent, showing significant inflammatory cell infiltration in the COPD group. After EA treatment, the number of macrophages and T lymphocytes was reduced.
Changes in Inflammatory Factors and Oxidative Stress Indicators:
In the COPD group, serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were elevated, antioxidant enzyme activity was reduced, and lipid peroxidation product MDA levels were increased. EA-3mA treatment significantly decreased the levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, while increasing the level of IL-10. It also enhanced the activity of SOD and GSH-Px in serum and lung tissue, and reduced MDA levels. EA-1mA treatment had a smaller effect on cytokine levels, with only some improvement observed in antioxidant indicators in the serum.
3.2 Transcriptomic Analysis Results
Differentially Expressed Genes Screening:
RNA-Seq analysis identified a total of 1,101 differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Hierarchical clustering showed distinct gene expression patterns between the COPD group and the NC group, with the EA-3mA group showing higher similarity to the NC group, whereas the EA-1mA group showed greater divergence. Venn diagram analysis revealed that, compared to the COPD group, the EA-1mA group upregulated 94 genes, and the EA-3mA group upregulated 255 genes, with 32 genes overlapping. Additionally, 63 genes upregulated in the COPD group compared to the NC group were reversely regulated following EA treatment. Specific genes that were only expressed in certain EA groups were also identified, such as Msr1 and Slc26a4, which were downregulated only in the EA-1mA group, and Pde3a and Bmp6, which were upregulated only in the EA-3mA group.
Functional Annotation Analysis:
GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that DEGs in the COPD group were mainly enriched in complement and coagulation cascades, phagosome, circadian rhythm, and other pathways. The EA-3mA group also showed enrichment in these pathways, and additionally, showed specific enrichment in cholinergic synapse, glutamatergic synapse, and axon guidance pathways. The EA-1mA group, compared to the COPD group, mainly enriched pathways associated with inflammation and immune responses, such as neutrophil extracellular trap formation, phagosome, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) signaling pathways.
3.3 WGCNA Analysis Results
WGCNA analysis divided the 1,101 DEGs into 5 modules. The MEblue module was negatively correlated with FEV/FVC ratio and serum SOD levels, and positively correlated with serum MDA levels. This module contained genes such as Aqp9, Trem1, Mrc1, and Gpnmb, which were downregulated in both EA intensities. The MEblue and MEbrown modules were negatively correlated with serum SOD levels, with Msr1 and Slc26a4 specifically restored in the EA-1mA group. The MEturquoise module was negatively correlated with serum IL-1β levels and contained genes such as Pde3a and Bmp6, which were specifically upregulated in the EA-3mA group. RT-qPCR and WB results confirmed that the expression trends of these genes were consistent with the sequencing results.
3.4 Target Gene Selection and Analysis
Based on the analysis and literature review, Mrc1, Gpnmb, Trem1, and Aqp9 were selected as target genes. These genes were significantly upregulated in the COPD model and downregulated following EA treatment. They may participate in the pathogenesis of COPD by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and tissue remodeling processes, making them potential therapeutic targets for EA treatment of COPD.
4. Research Conclusions
Both 1mA and 3mA electroacupuncture stimulation intensities induced different gene expression patterns in the COPD rat model, involving both shared and specific enrichment pathways. Genes such as Mrc1, Gpnmb, Trem1, and Aqp9 may serve as potential therapeutic targets, but further research is needed to explore their functional roles in COPD. This study provides transcriptomic evidence for a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying electroacupuncture treatment for COPD.
During the study, several scientific instruments were used.
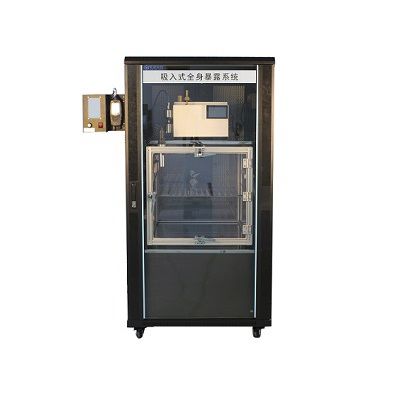
1. Tow-Int Tech Whole-Body Exposure System (CSM-100C, Tow-Int Tech, Shanghai, China)
It is used to expose rats to cigarette smoke for the establishment of the COPD rat model.
COPD Model Establishment Process:
Equipment Parameter Settings:
During the experiment, the rats were placed in an exposure chamber, where they were exposed to a controlled cigarette smoke environment according to a specific program.
Exposure Time and Cycles:
The experiment lasted for 12 weeks, during which the rats were exposed to cigarette smoke for 2 hours daily (in two 1-hour sessions). In total, the rats were exposed to smoke from 30 cigarettes. Each cigarette contained 11 mg of tar and 1.1 mg of nicotine.
Simulating the Pathological Environment of COPD:
By exposing the rats to cigarette smoke for an extended period, the model mimicked the pathological process of COPD caused by chronic smoking in humans. The harmful substances in cigarette smoke induced chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in the rats' lungs, leading to pulmonary pathological changes similar to those seen in COPD patients, such as alveolar damage, small airway inflammation, and obstruction.
Enhancing Inflammatory Response with LPS Injection:
At specific time points (days 1, 31, and 61), the rats were intratracheally injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). LPS, as an inflammatory stimulant, further enhanced the lung inflammation response, making the rat model more closely resemble the pathological features of human COPD. This approach helped establish a more stable and reliable COPD animal model for subsequent research on the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of electroacupuncture in treating COPD.
2. Animal Pulmonary Function Testing System:
The system is used to assess the pulmonary function of rats, including forced expiratory volume (FEV), forced vital capacity (FVC), and other indicators, to evaluate the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on the lung function of COPD rats.
Pulmonary Function Testing Process:
Rats were anesthetized and underwent tracheotomy. The system is equipped with a ventilator that can automatically control the animal's breathing pattern, allowing for different pulmonary function tests to be performed.
Monitored Parameters:
The tested parameters include the forced expiratory volume at 0.1 seconds (FEV0.1), forced expiratory volume at 0.3 seconds (FEV0.3), and forced vital capacity (FVC). The ratio of FEV to FVC (FEV/FVC) is calculated to assess lung function.
These parameters are used to evaluate the lung function status of rats, helping to understand the pulmonary function changes in the COPD rat model, as well as the impact of different intensities of electroacupuncture treatment on lung function.
Reference
Liu, Lu, et al. "Transcriptomic Insights into Different Stimulation Intensity of Electroacupuncture in Treating COPD in Rat Models." Journal of Inflammation Research (2024): 2873-2887.
Contact us now!
We are committed to making your research easier, more accurate, and more efficient and helping you build confidence in your data! We have provided services for a large number of customers and have rich experiences in offering customized, professional solutions according to your needs.